In modern manufacturing, thermoplastic presses have become indispensable core tools in various industrial fields. With the development of materials science and the continuous optimization of processing technology, the application range of thermoplastics is constantly expanding, from automobiles and aerospace to electronics and consumer goods manufacturing, its influence is becoming increasingly significant.
Content
- 1 Working Principle of Thermoplastic Molding Equipment
- 2 Equipment Structure and Core Component Analysis
- 3 Process Optimization and Material Adaptability
- 4 Application Areas of Thermoplastic Molding Equipment
- 5 FAQ (Frequently Asked Questions)
- 5.1 Q: What is the difference between thermoplastic molding equipment and traditional injection molding machines?
- 5.2 Q: How does the equipment ensure product precision during production?
- 5.3 Q: Do different materials require different equipment parameters?
- 5.4 Q: What are the future development trends for thermoplastic molding equipment?
Working Principle of Thermoplastic Molding Equipment
The core of thermoplastic molding equipment lies in heating plastic materials at high temperatures to a plastic state, and then shaping the final product through pressure or mold forming processes. This process involves three key stages: heat conduction, material flow, and cooling and solidification. The equipment precisely controls temperature and pressure to ensure that the thermoplastic is heated uniformly in a short time, while maintaining the smoothness and uniformity of the mold's inner surface, thereby ensuring the precision and surface quality of the product.
In terms of process implementation, thermoplastic molding equipment is typically equipped with high-precision heating plates and pressure systems. The heating plates can adjust the temperature gradient according to the material characteristics, ensuring that the plastic molecules undergo controllable flow and rearrangement during heating. The pressure system applies uniform mechanical force to ensure the material fully conforms to the mold contour, achieving the molding of complex geometries. The cooling process is equally crucial, rapidly cooling to lock in the material's shape and prevent warping or stress concentration caused by thermal expansion and contraction.

Equipment Structure and Core Component Analysis
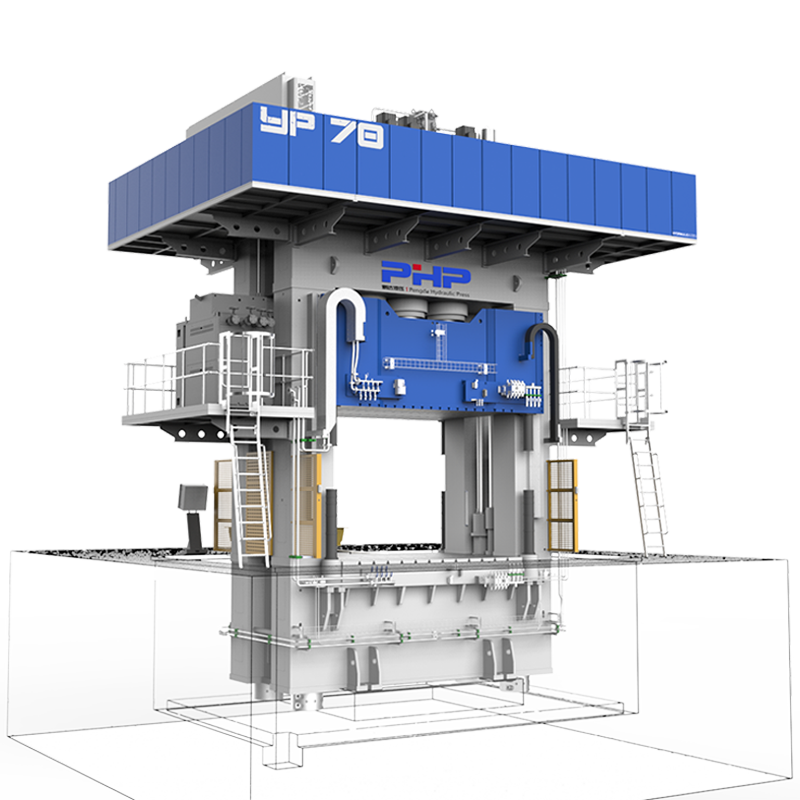
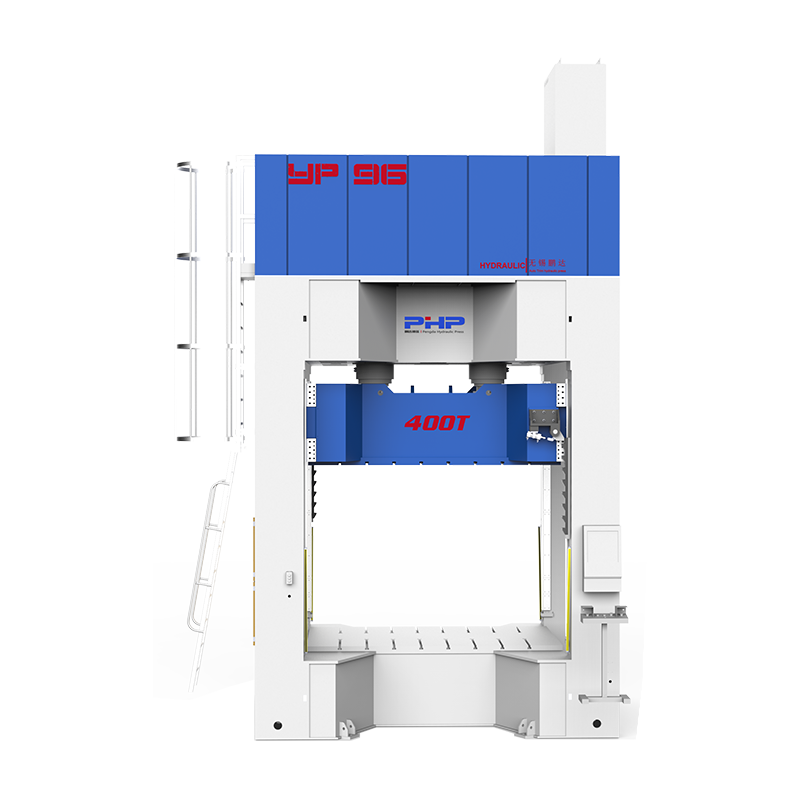
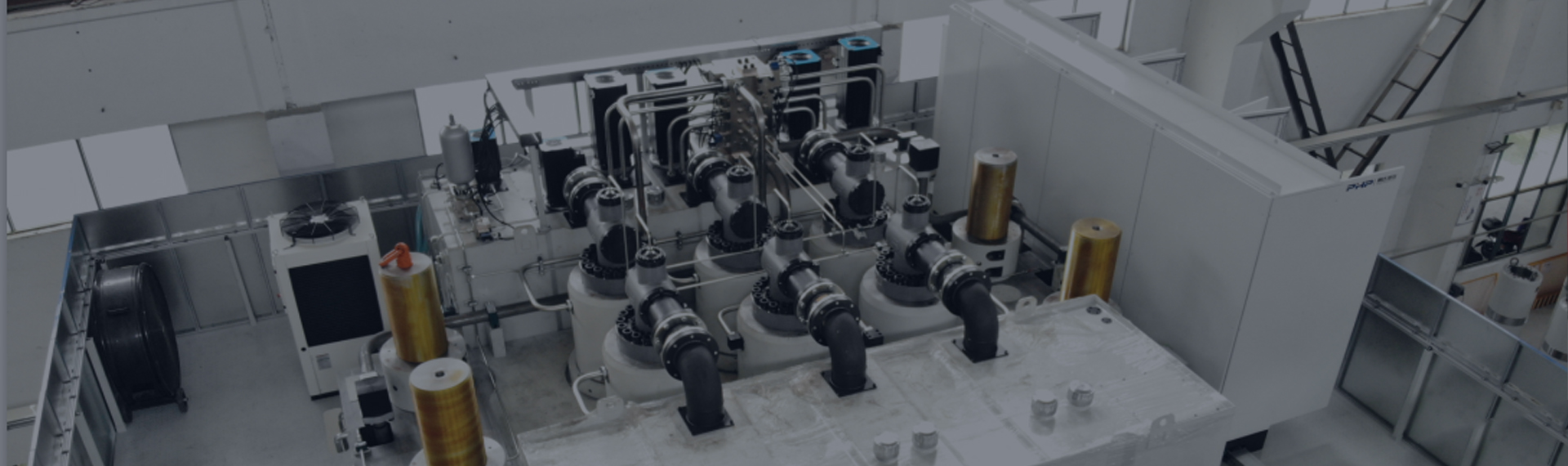
Thermoplastic molding equipment emphasizes a high degree of integration between mechanical structure and thermal management. Its main components include a heating system, a pressure system, a mold fixing device, and a control system. The heating system not only needs to provide uniform heat but also requires rapid response capabilities to adapt to workpieces of different materials and thicknesses. The pressure system includes hydraulic, mechanical, or pneumatic drive devices, whose function is to ensure uniform material distribution and close adhesion to the mold surface during the molding process.
The control system is the intelligent core of modern thermoplastic molding equipment. Through real-time monitoring and automatic adjustment of parameters such as temperature, pressure, and time, the equipment can achieve high precision and stability in multi-batch production. Simultaneously, advanced control algorithms can dynamically optimize the molding process based on the material's physical properties, significantly improving product consistency and yield.
Process Optimization and Material Adaptability
The efficient operation of thermoplastic molding equipment relies on process optimization and material matching. Different types of thermoplastics, such as polypropylene, polycarbonate, and polyamide, have different melting points, flowability, and heat sensitivity. Equipment requires fine-tuning of temperature profiles, pressurization methods, and cooling rates based on material characteristics. Through proper process optimization, not only can production efficiency be improved, but equipment lifespan can also be extended and energy consumption reduced.
Modern thermoplastic molding equipment increasingly emphasizes intelligent control. Through sensors and data acquisition systems, the equipment can monitor temperature distribution, pressure changes, and material flow states in real time during the molding process. Combined with big data analytics and machine learning algorithms, companies can establish material performance databases and process models to achieve consistent control and process improvement in mass production.
Application Areas of Thermoplastic Molding Equipment
Thermoplastic molding equipment is used in almost all manufacturing fields requiring high-precision plastic parts. In the automotive industry, the equipment can produce high-strength, lightweight internal components and shells. In electronics and consumer goods manufacturing, it enables the precision molding of complex structures, ensuring a balance between aesthetics and functionality. In the aerospace and medical device fields, thermoplastic molding equipment, with its high precision and controllability, has become the preferred choice for manufacturing high-performance components.
With the advancement of sustainable development and green manufacturing concepts, the performance of this equipment in energy conservation, emission reduction, and material recycling is receiving increasing attention. Through precise temperature control and pressure management, thermoplastic molding equipment can not only reduce waste generation but also achieve efficient reuse of some recycled materials.
FAQ (Frequently Asked Questions)
Q: What is the difference between thermoplastic molding equipment and traditional injection molding machines?
A: Thermoplastic molding equipment emphasizes molding plastic sheets or plates through high temperature and pressure, suitable for large-area or high-strength parts, while traditional injection molding machines are mainly used for injecting molten plastic into molds, suitable for mass production of small parts.
Q: How does the equipment ensure product precision during production?
A: Through a high-precision temperature control system, uniform pressure application, and real-time monitoring and control, the equipment ensures uniform material flow and cooling, thereby improving product dimensional stability and surface quality.
Q: Do different materials require different equipment parameters?
A: Yes, different thermoplastics have different melting points, flowability, and heat sensitivity. Therefore, the equipment needs to be adjusted for different materials, including temperature profiles, pressure distribution, and cooling rates.
Q: What are the future development trends for thermoplastic molding equipment?
A: Intelligent control, energy saving, multi-functional molding, and high-performance material processing capabilities are the core trends for future equipment development.

 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 Español
Español Português
Português Deutsch
Deutsch русский
русский